Set Up On-Prem Deployment Disaster Recovery
Note
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the maximum acceptable amount of time since the last data recovery point. If an RPO of 1 to 24 hours is acceptable, then Chef recommends using a typical backup and restore strategy for your disaster recovery plan.
Set these two clusters in different data centers or cloud provider regions.
Requirements
- Two identical clusters located in different data centers or cloud provider regions
- Network accessible storage (NAS), object store (S3,MinIO,Google Cloud Storage), available in both data centers/regions
- Ability to schedule jobs to run backup and restore commands in both clusters. We recommend using corn or a similar tool like anacron.
In the above approach, there will be 2 identical clusters
- primary cluster (or production cluster)
- disaster recovery cluster
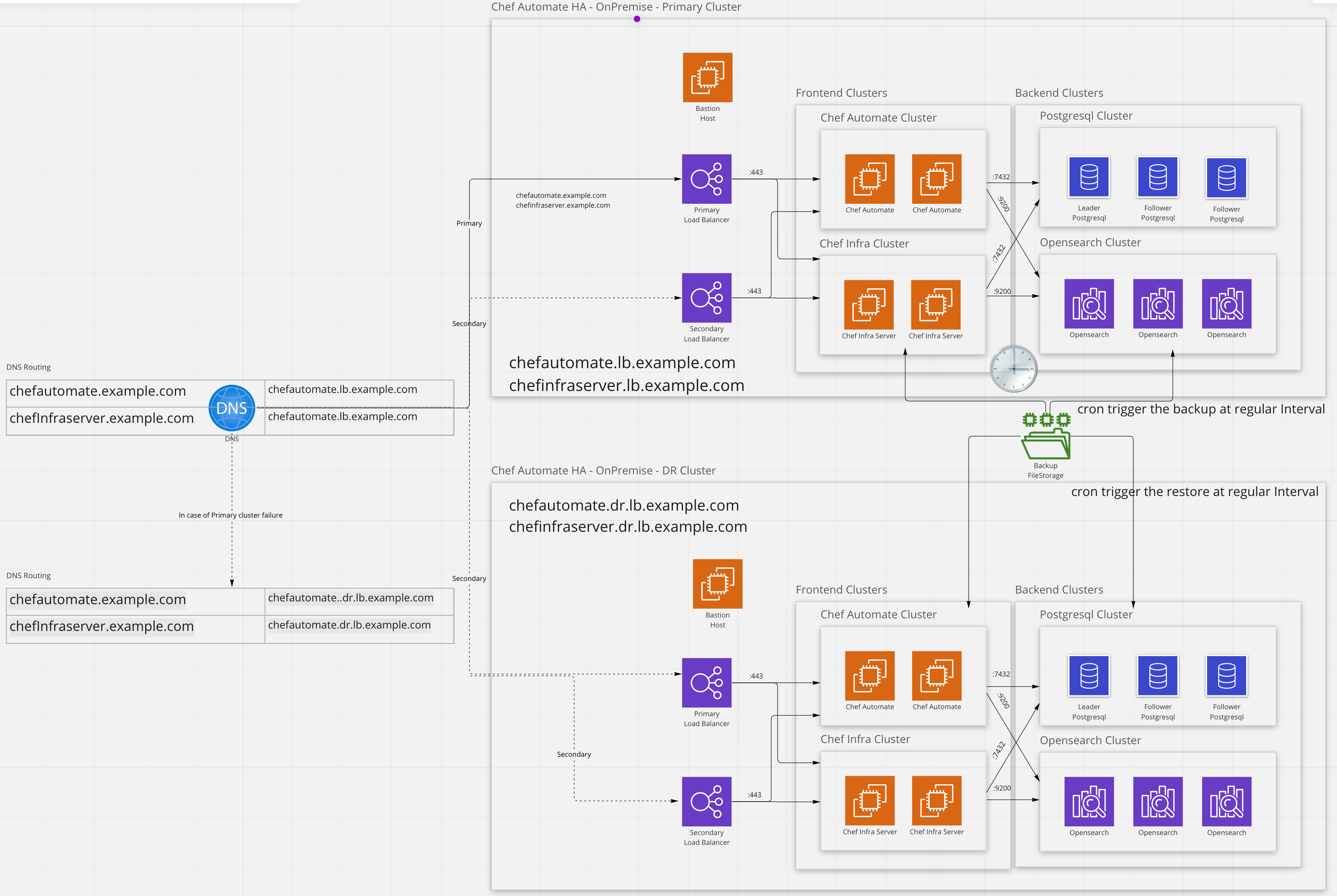
The primary cluster will be active and regular backups will be performed using chef-automate backup create. At the same time, the disaster recovery cluster will be restoring the latest backup data using chef-automate backup restore.
When a failure of the primary cluster occurs, fail-over can be accomplished through updating DNS records to the DR cluster, alternatively, many commercial load balancers can be configured to handle routing traffic to a DR cluster in the event of a failure.
Caveat with the above approach
- Running two parallel clusters can be expensive.
- The amount of data loss will depend on how frequently backups are performed in the primary cluster.
- Changing DNS records from the primary load balancer to the disaster recovery load balancer can take time to propagate through the network.
Set up the production and disaster recovery cluster
Deploy the primary cluster following the deployment instructions by clicking here.
Deploy the disaster recovery cluster into a different data center and region using the same steps as the primary cluster.
Do the backup configuration as explained in backup section for file system or object storage.
Note
On the primary cluster
- From one of the Chef Automate nodes, configure a cronjob to run the
chef-automate backupcommand at a regular interval. The sample cron for backup looks like:
chef-automate backup create --no-progress > /var/log/automate-backups.log- Create a bootstrap bundle; this bundle captures any local credentials or secrets that aren’t persisted to the database. To create the bootstrap bundle, run the following command in one of the Automate nodes:
chef-automate bootstrap bundle create bootstrap.abb- Copy
bootstrap.abbto all Automate and Chef Infra frontend nodes in the disaster recovery cluster.
Note
- Suggested frequency of backup and restore jobs is one hour. Be sure to monitor backup times to ensure they can be completed in the available time.
- Make sure the Restore cron always restores the latest backed-up data.
- A cron job is a Linux command used to schedule a job that is executed periodically.
To clean the data from the backed-up storage, either schedule a cron or delete it manually.
- To prune all but a certain number of the most recent backups manually, parse the output of chef-automate backup list and apply the command chef-automate backup delete. For example:
export KEEP=10; export HAB_LICENSE=accept-no-persist; chef-automate backup list --result-json backup.json > /dev/null && hab pkg exec core/jq-static jq "[.result.backups[].id] | sort | reverse | .[]" -rM backup.json | tail -n +$(($KEEP+1)) | xargs -L1 -i chef-automate backup delete --yes {}
- From one of the Chef Automate nodes, configure a cronjob to run the
On disaster recovery cluster
- Install
bootstrap.abbon all the frontend nodes (Chef-server and Automate nodes) by running the following command:
sudo chef-automate bootstrap bundle unpack bootstrap.abbWe don’t recommend creating backups from the disaster recovery cluster unless it has become the active cluster and receiving traffic from the clients/nodes.
Stop all the services on all Automate and Chef Infra frontend nodes using the following command:
systemctl stop chef-automateMake sure both backup and restore cron are aligned.
Run the following command in one of the Automate nodes to get the IDs of all the backups:
chef-automate backup listConfigure the cron that triggers the
chef-automate backup restoreon one of the Chef Automate nodes.To run the restore command, you need the airgap bundle. Get the Automate HA airgap bundle from the location
/var/tmp/in Automate instance. For example:frontend-4.x.y.aib.In case the airgap bundle is not present at
/var/tmp, it can be copied from the bastion node to the Automate frontend nodeRun the command at the Automate node of Automate HA cluster to get the applied config:
sudo chef-automate config show > current_config.toml- Add the OpenSearch credentials to the applied config. If using Chef Managed OpenSearch, add the config below into
current_config.toml(without any changes).
[global.v1.external.opensearch.auth.basic_auth] username = "admin" password = "admin"- In the disaster recovery cluster, use the following sample command to restore the latest backup from any Chef Automate frontend instance.
For S3/MinIO execute the following command from the Bootstrapped Automate node to restore:
id=$(sudo chef-automate backup list | tail -1 | awk '{print $1}') sudo chef-automate backup restore /mnt/automate_backups/backups/$id/ --patch-config current_config.toml --airgap-bundle /var/tmp/frontend-4.x.y.aib --skip-preflightFor GCS execute the following command from the Bootstrapped Automate node to restore:
id=$(sudo chef-automate backup list | tail -1 | awk '{print $1}') sudo chef-automate backup restore gs://bucket_name/path/to/backups/BACKUP_ID --patch-config current_config.toml --airgap-bundle /var/tmp/frontend-4.x.y.aib --skip-preflight --gcs-credentials-path "path/to/googleServiceAccount.json"`Sample cron for restoring backup saved in object storage (S3/MinIO) looks like this:
id=$(chef-automate backup list | grep completed | tail -1 | awk '{print $1}') sudo chef-automate backup restore <backup-url-to-object-storage>/automate/$id/ --patch-config /path/to/current_config.toml --airgap-bundle /var/tmp/frontend-4.x.y.aib --skip-preflight --s3-access-key "Access_Key" --s3-secret-key "Secret_Key"Sample cron for restoring backup saved in object storage (GCS) looks like this:
id=$(chef-automate backup list | grep completed | tail -1 | awk '{print $1}') sudo chef-automate backup restore <backup-url-to-object-storage>/automate/$id/ --patch-config /path/to/current_config.toml --airgap-bundle /var/tmp/frontend-4.x.y.aib --skip-preflight --gcs-credentials-path "path/to/googleServiceAccount.json"
- Install
Switch to disaster recovery cluster
Steps to switch to the disaster recovery cluster are as follows:
Stop the backup restore cron.
Start the services on all the Automate and Chef Infra frontend nodes, using below command
systemctl start chef-automateUpdate the Automate FQDN DNS entry to resolve to the disaster recovery load balancer.
The disaster recovery cluster will be the primary cluster, it may take some time for DNS changes to fully propagate.
Setup backup cron to start taking backups of the now active cluster.